RADIUS Authentication
RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) is a networking protocol that provides centralized Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) management for users who connect and use a network service. RADIUS is commonly used for managing access to network resources, such as Wi-Fi networks, virtual private networks (VPNs), and other types of networked services.
RADIUS operates in a client-server architecture. Network devices (routers, switches, firewalls, VPNs, access points) act as RADIUS clients and forward authentication requests to the RADIUS server. The RADIUS server processes these requests, authenticates the user, and communicates the authorization and accounting information back to the client.
The InstaSafe Secure Access (ISA) supports RADIUS authentication along with Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) over PAP & CHAP authentication methods. The ISA platform acts as a RADIUS server and receives authentication requests from RADIUS clients, such as routers, firewalls or VPNs, verifies the credentials of the user, and returns an authorization decision to the client.
This article provides a step-by-step guide on configuring an authentication profile that integrates RADIUS servers for user provisioning and authentication.
RADIUS Authentication is designed to provide the below features:
1. Centralized Authentication
By acting as a central authentication hub, RADIUS allows organizations to manage user credentials and policies in a single location, streamlining the authentication process across multiple systems.
2. Enhanced Security
It enforces robust security protocols (e.g., EAP, CHAP, and PAP) and supports encrypted data exchanges to protect user credentials during authentication.
3. Flexibility in Deployment
RADIUS is protocol-agnostic, meaning it can integrate with various network components, including wireless access points, VPN servers, and firewalls, making it adaptable for different environments.
4. Accountability and Monitoring
RADIUS provides detailed logs and audit trails for authentication and network access, helping organizations maintain accountability and detect anomalies.
5. Scalability
It is designed to support enterprise environments with a large number of users and devices, ensuring consistent performance as organizations grow.
Use Cases for RADIUS Authentication
1. Wireless Network Access Control
In enterprise networks, RADIUS is often used to authenticate and authorize users accessing the Wi-Fi network.
Example: Employees use their corporate credentials to connect to the secure office Wi-Fi. The RADIUS server validates the credentials and ensures the user is authorized to access the network.
2. VPN Authentication RADIUS is integrated with VPN servers to authenticate remote users, ensuring secure access to the internal corporate network.
Example: A remote employee connects to the company’s VPN. The RADIUS server verifies their username and password before granting access to internal systems.
3. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Integration
RADIUS supports the addition of MFA for a stronger layer of security during user authentication.
Example: A user logs in to a system and is prompted to enter a one-time passcode (OTP) in addition to their username and password. The RADIUS server manages both authentication factors.
4. Network Device Administration
RADIUS can control and monitor access to critical network devices like routers, switches, and firewalls.
Example: A network engineer accesses a router. The RADIUS server authenticates their credentials and logs the access for accountability.
5. Guest User Management
In environments like hospitality or education, RADIUS can manage temporary or limited network access for guests.
Example: A university provides guest Wi-Fi access to visitors. The RADIUS server ensures guests receive time-limited access credentials while protecting the main network.
6. Access Control for IoT Devices
RADIUS can be used to authenticate IoT devices, ensuring they are authorized to connect to a network.
Example: An industrial IoT sensor attempts to connect to the company’s network. The RADIUS server validates its device certificate before allowing access.
7. Secure Contractor and Partner Access
External collaborators can access specific systems or networks via RADIUS authentication while adhering to organizational policies.
Example: A contractor accesses the company’s file-sharing system through a secure VPN connection authenticated by RADIUS.
InstaSafe AD Integration Guide for Radius
The following are the steps to use AD authentication with InstaSafe Secure Access
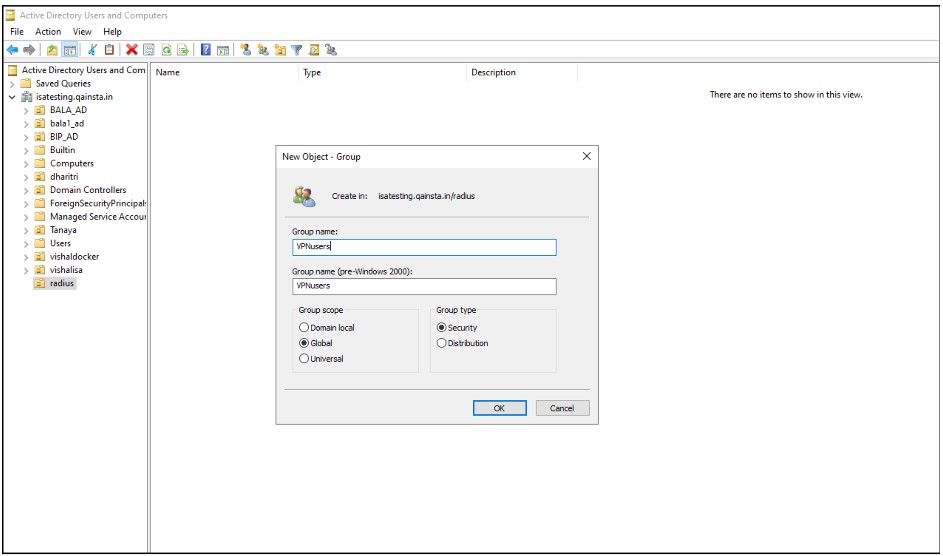
1. Create a security group
Create a security group in Active Directory Users and Computers called VPNusers. Everyone could have access but it's a good policy to identify the VPN Users and have granular access control.
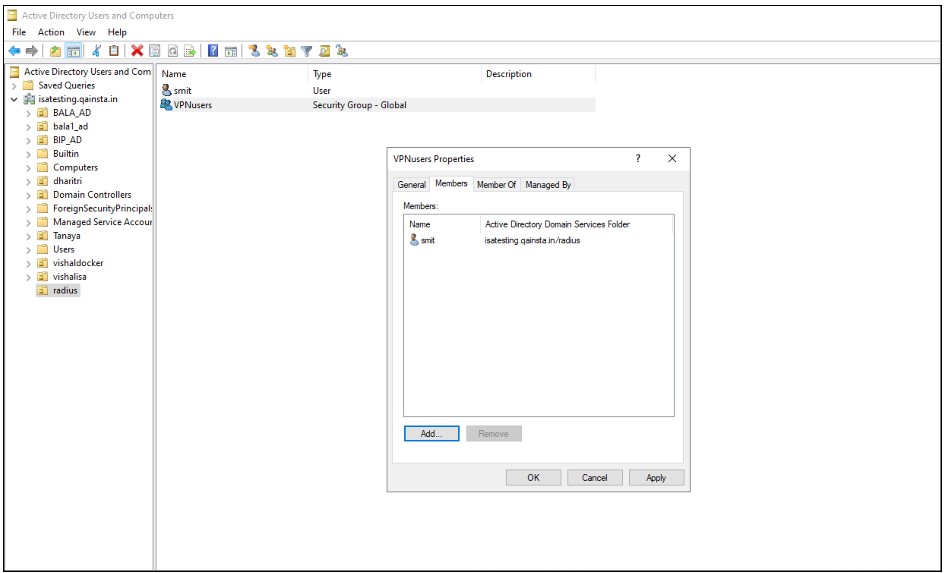
2.Add Users to Security Group
Add user accounts that use the InstaSafe VPN to this group.
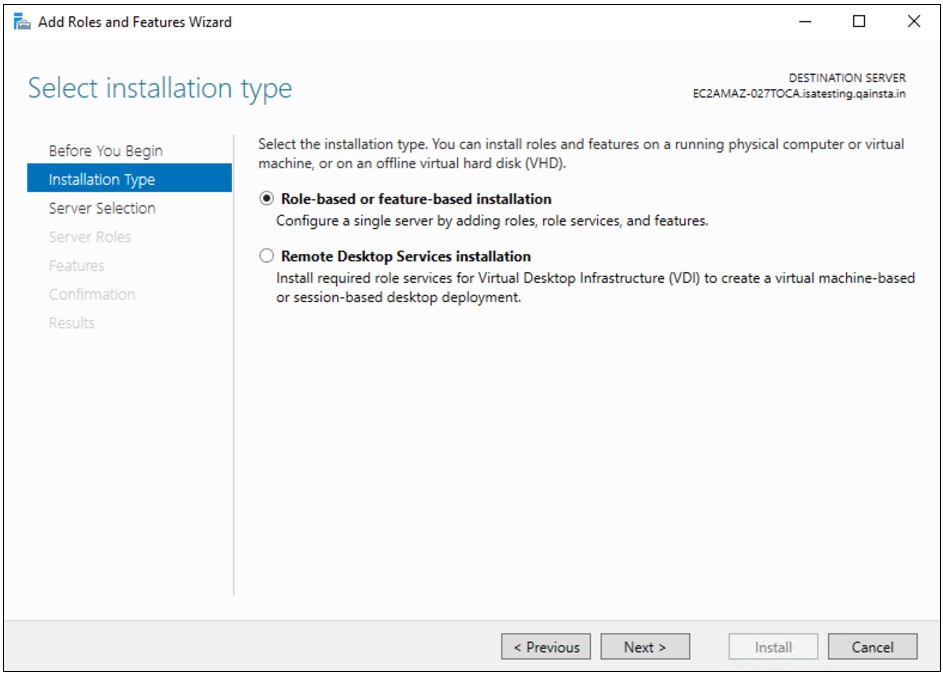
3.Add “Network Policy and Access Service” Role
On the Active Directory Check if the “Network Policy and Access Services” role exists under Roles in Server Manager. Otherwise, click right-click Roles and select Add Role.
Click Next to add role in the wizard
Select “ Network Policy and Access Services” under the Roles to be added and click Next
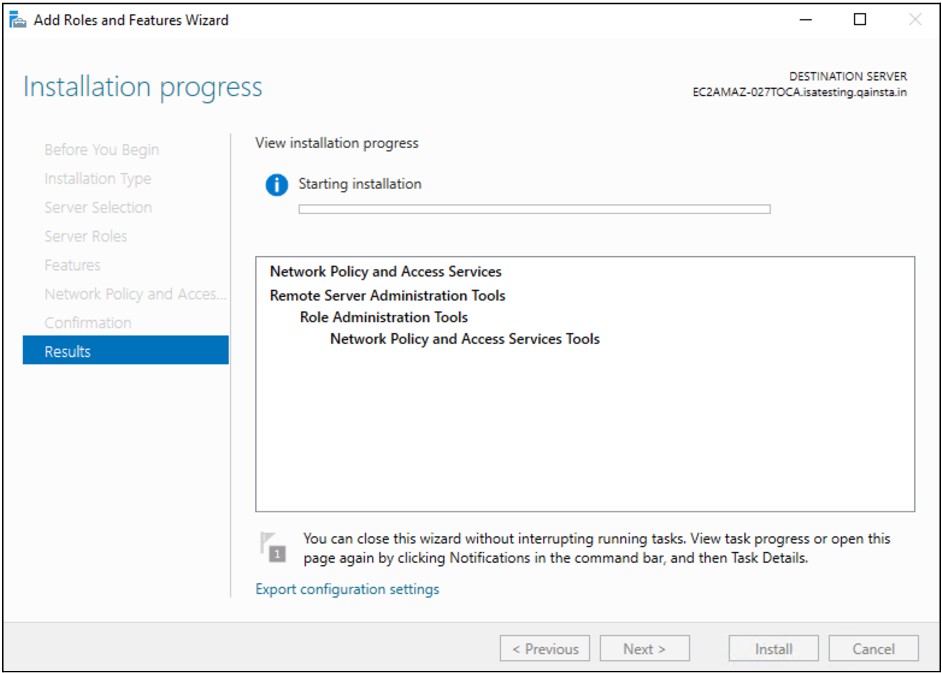
Under Role Services, select Network Policy Server and Click Next
Once the Role is added, it appears under Roles in the Server Manager
4. Add Radius Client
Expand the Network Policy and Access Services node, go to NPS (Local) > RADIUS Clients and Servers, right-click RADIUS Clients and choose New
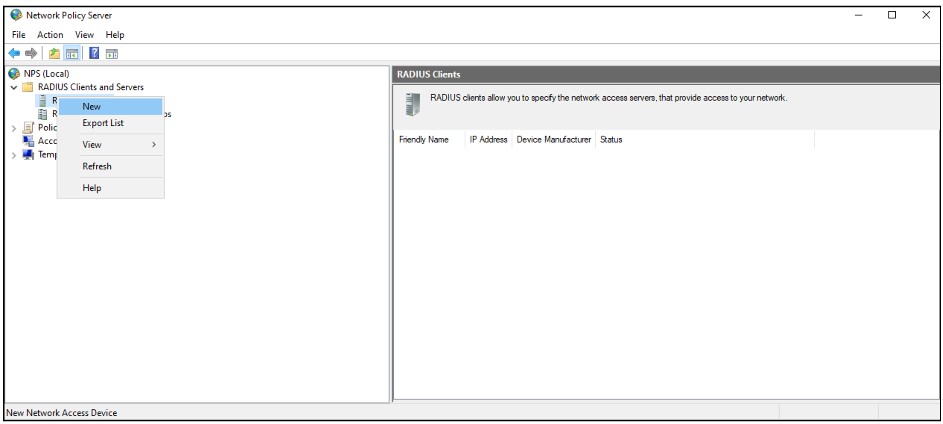
Fill in the below fields
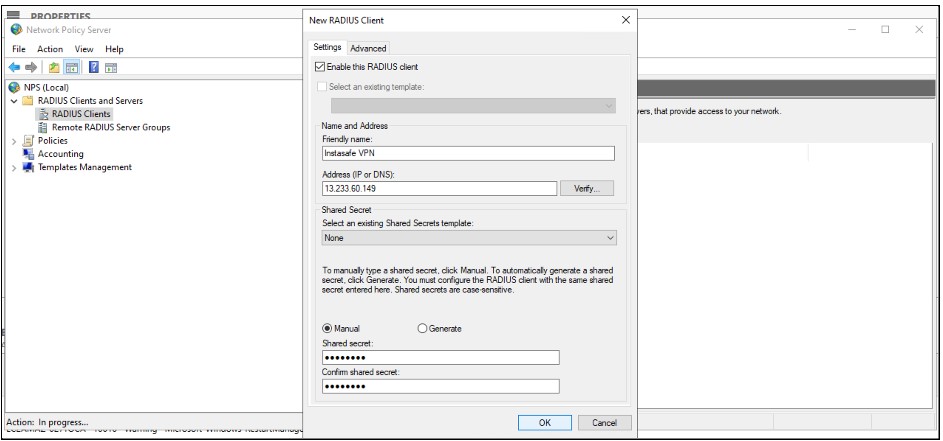
Friendly name: Enter InstaSafe VPN or anything deemed appropriate
Address (IP or DNS): Enter the LAN IP address of the InstaSafe Gateway. For example: 192.168.1.77. Please confirm the IP address from the InstaSafe Support Team
Shared Secret: Select Manual, set a password and save the shared secret.
This secret is required to be configured later on the my.instasafe.net portal.
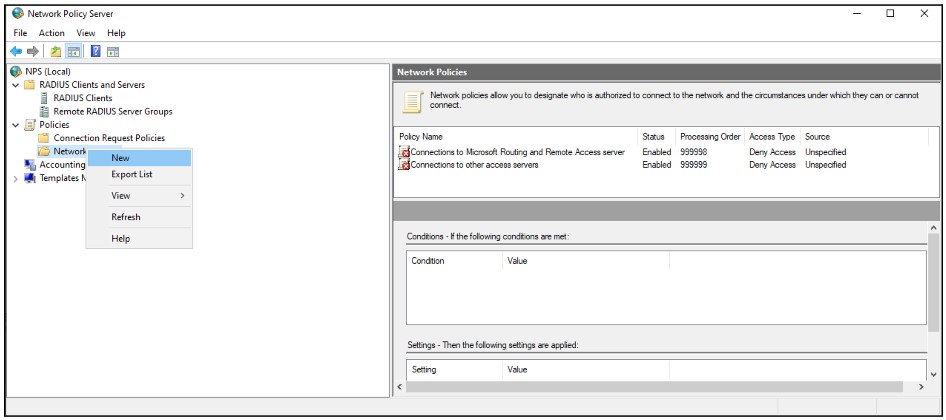
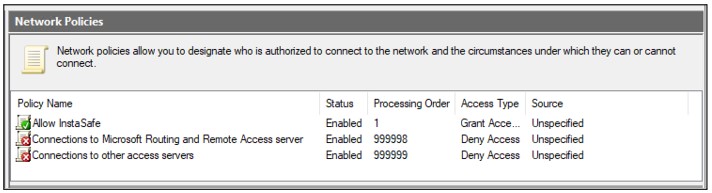
5. Add Network Policy
Under NPS (Local) > Policies right-click Network Policies and select New
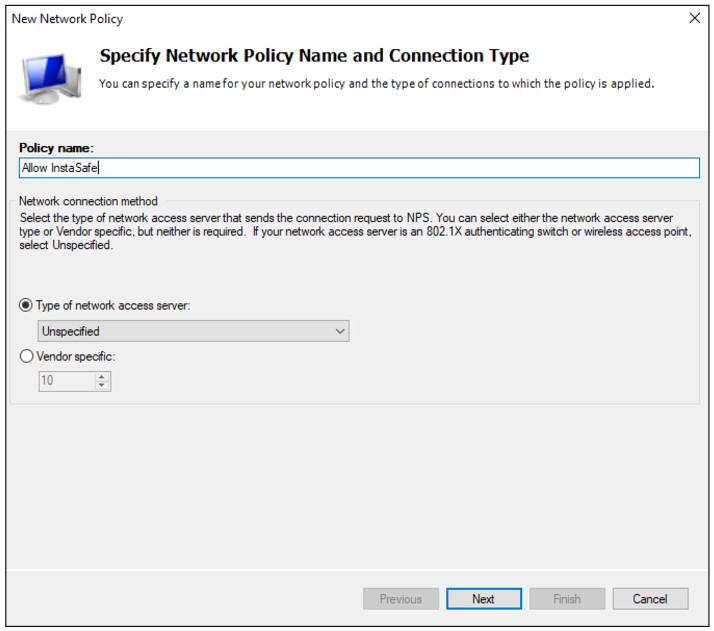
In the Policy name field, enter Allow InstaSafe.
Type of network access server: Unspecified
Click Next
In the Specify Conditions window, click Add
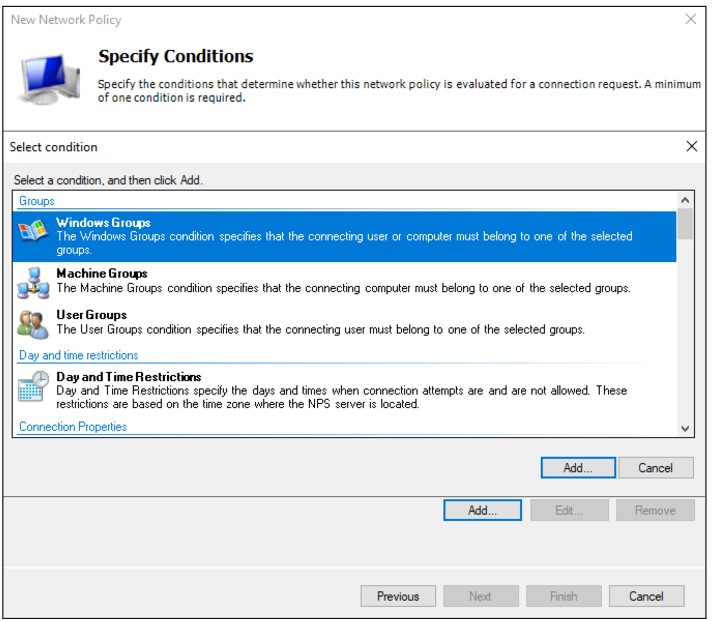
Select Windows Groups and click Add
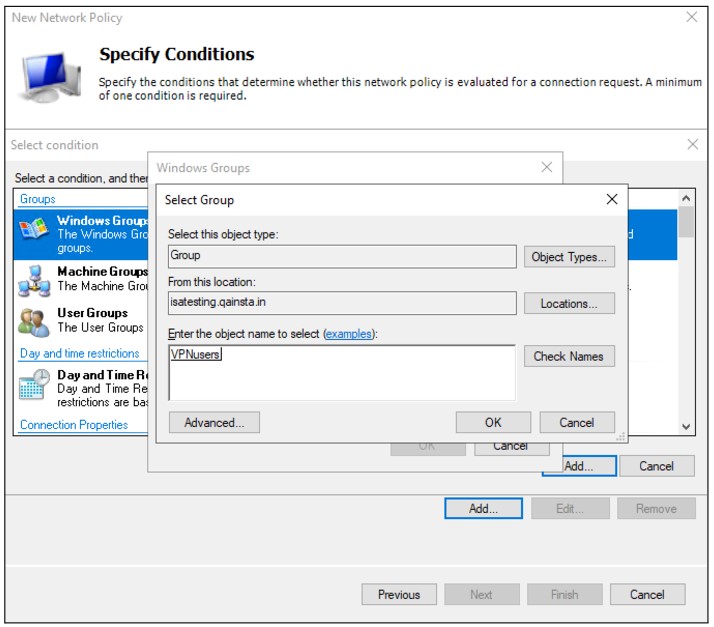
Click Add Groups and add the group VPNusers (or whatever group is needed)
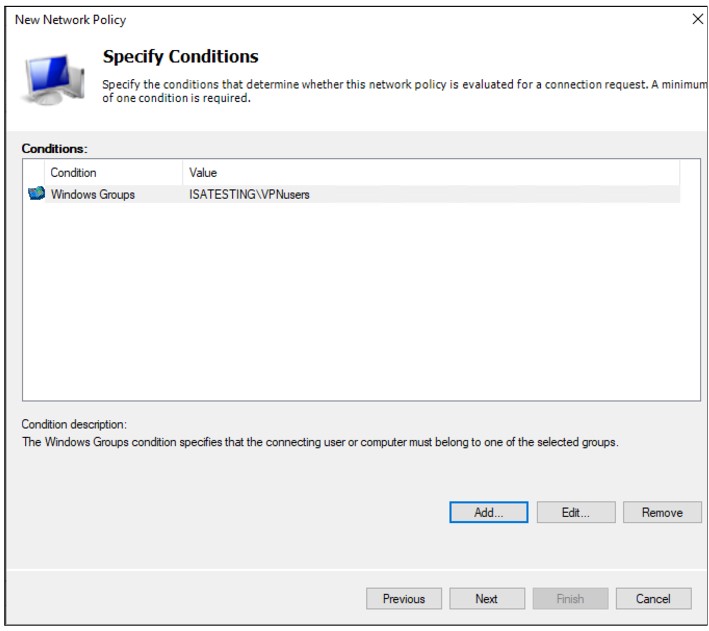
Back in the Specify Conditions window, click Next
Select Access granted
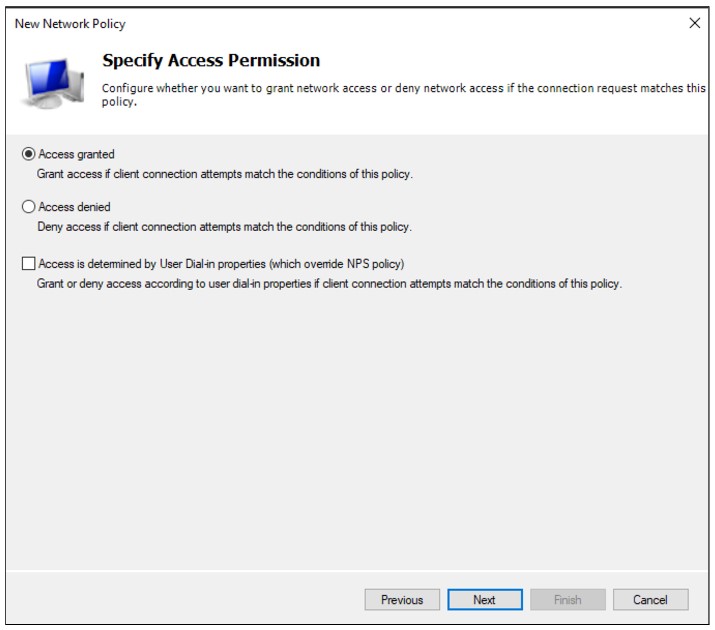
Put the new policy before policies preventing the connection. Please note the Processing Order should be high for “Allow InstaSafe” Policy.
6. Configure Authentication Methods
In the Configure Authentication Methods window, check Unencrypted authentication (PAP, SPAP)
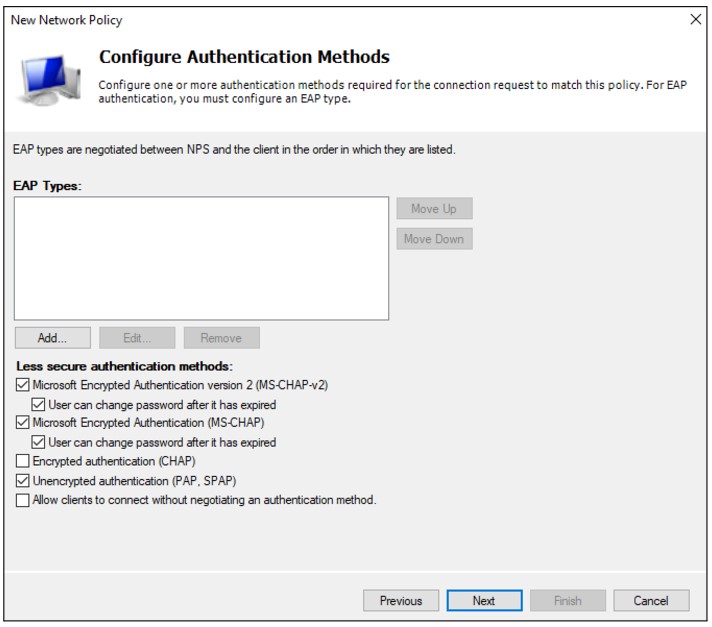
Skip the next wizard window (Constraints) and click Next, Next, Finish until the end.
7. Configuring RADIUS Authentication Profile on the ISA Web Console
-
Log in to the ISA web console using administrator credentials.
-
Click on AUTHENTICATION PROFILES in the left-hand menu.
-
Under AUTHENTICATION PROFILES click on RADIUS.
-
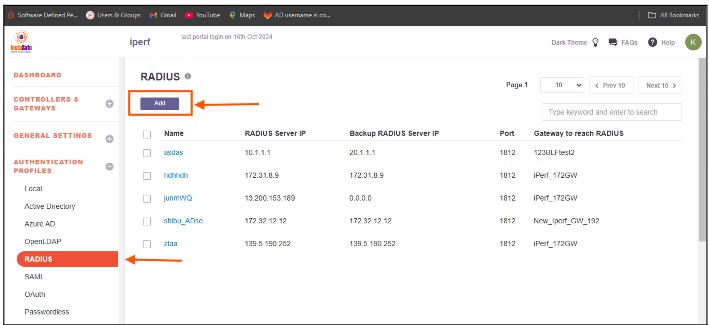
On the RADIUS page, under RADIUS Profile, click on the Add button.
-
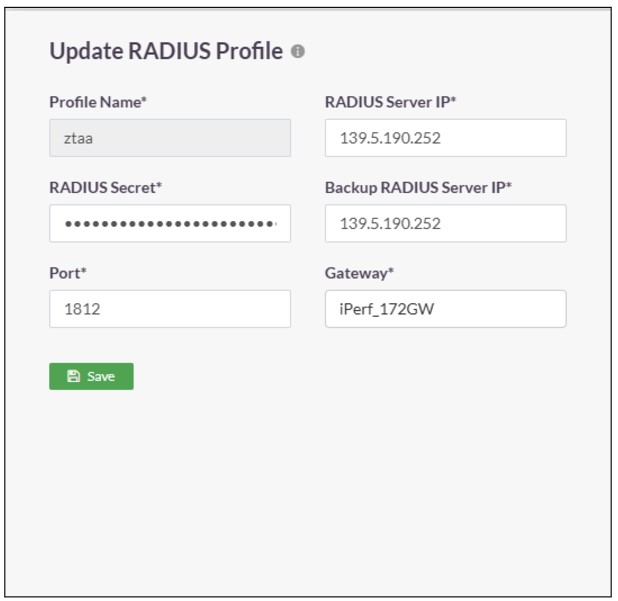
In the Create RADIUS Profile window, enter the following information under each field:
- Profile Name: Enter a descriptive name for this profile. The name must not contain spaces. This field is mandatory.
- Gateway to reach RADIUS: Select the Gateway name through which the OpenLDAP server can be accessed. For example, "Gateway BLR-Data-Centre." This field must be selected from the available options
- RADIUS Server IP: Enter the private IP address of the RADIUS server. This field must be filled-in
- Backup RADIUS Server IP: Enter the private IP address of the backup RADIUS server
- Port: Enter the port number Open LDAP server for example Radius server port : 1812
- Radius Secret: Enter the shared secret configured manually while adding the radius client in the “Network Policy and Access Service”
-
Click on Save to create this profile. This will create a RADIUS profile and the new profile will be displayed on the page.
-
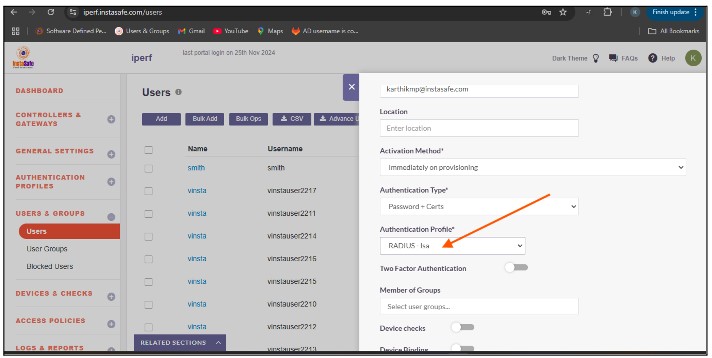
Open the user profile And Assign the Authentication Profile to the user profile.
To verify that InstaSafe Secure Access is using AD authentication, please start the InstaSafe Agent and enter the AD username in the email format (username@domain) and the AD password for the user. If the connection is successful, the AD integration is complete. If the connection is unsuccessful, please contact support@instasafe.com or call InstaSafe Support for assistance.